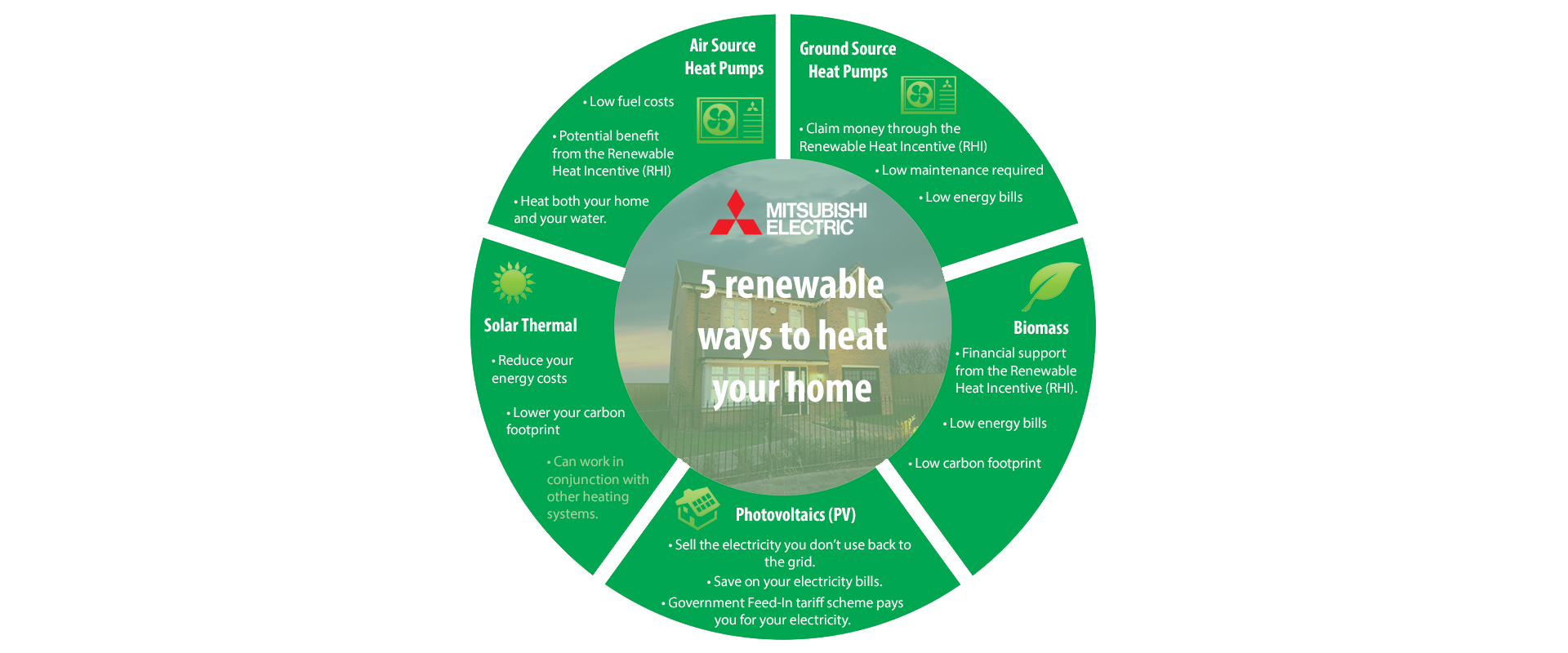
Air Source Heat Pumps
Air Source Heat Pumps use electric to harvest ‘free’ renewable energy from the outdoor air to heat a refrigerant inside the outdoor unit. This in turn heats water and space heating for your home and will work even in sub-zero temperatures. We’ve all been using heat pump technology for decades in the form of our kitchen fridge and heat pumps for heating actually is essentially a fridge in reverse.
Ground Source Heat Pumps
Ground Source Heat Pumps take energy from the ground through pipes buried underneath your garden. They work in a similar way to air source heat pumps as they heat refrigerant which in turn heats your water and space heating. Ground source heat pumps can require a lot of space outside your house as the pipework needs to be buried in trenches. Alternatively, they need deep bore holes down into the earth to take thermal energy from under your home.
5 renewable ways to heat your home
By heating your home with renewable energy you could be making money through the RHI or FIT
Solar Thermal
Solar thermal heating absorbs the suns heat through tube panels on your roof to heat up water. This water is then pumped through a coil in your cylinder heating the water within it ready for you to turn on your taps. It is generally not recommended for use with radiators or underfloor heating in the UK due to the low levels of UV radiation in the winter so it would need to work in conjunction with another energy system. However, it can be a good way to supplement your existing heating and help reduce the energy needed for your hot water.
Biomass
Biomass is fuel derived from living, or recently living organisms that have stored sunlight as chemical energy. When burned, the energy in biomass is released as heat. In the UK the most popular biomass fuels is wood in the form of logs, pellets and wood chips. Biomass boilers tend to be larger than gas boilers and you need to have the space to store the fuel. You also need to remove the ash and have them maintained regularly.
Photovoltaics
Photovoltaics turn sunlight into electricity via solar panels in a process called the Photovoltaic effect. The stronger the sunshine the more electricity is produced however direct sunshine isn’t necessarily needed. The electricity produced can be used to power appliances in your household – meaning you don’t consume energy from the grid. If you produce more power than your household needs, electricity can be sold back to the grid through the Feed In Tariff scheme.
Gemma Lakin is a Marketing Specialist at Mitsubishi Electric
If you have any questions about this article or want to know more, please email us. We will contact the author and will get back to you as soon as we can.
Click here if you would like more information on air source heat pumps, including the award-winning Ecodan range.
